Copyright 2009
Introduction
Uterus functions has an important role in reproduction. It functions as a site for implantation of fertilized oveum and accomodates the growing fetus untill child birth. During child birth muscular layer of uterus helps in parturition.
Physiology:
Uterine physiology is influenced by hormones from hypothalamus-pituitary- ovarian axis. The details of endometrial changes will be discussed in a seperate section. The uterine tubes act as a site for fertilization of the ovum; the fertilized ovum than gets implanted in the uterine wall. Uterus under the effects of progestrone helps in maintenace of pregancy by redcing uterine contraction and bringing about favorable changes. In subsequent weeks placenta takes over the secretion of progesterone.
At child birth there is an increasing concentration of oxytocin secreted by posterior pituitary. There is an increased concentration of prostaglandins while PGE2 brings about softening of cervix, PGF2 cause contractions. Oxytocin causes the rhythmic contractions manifested as labor pains. The intermittent nature of these contraction helps in child birth without jeopardizing the blood supply to the uterus. Uterine fibres are in different layers external layers is arranged transversely, middle layers is irregular while inner layers is like a submucousal muscular layer. The lower segment and cervix are circular in layer. During labor upper uterine segment contract and retract which essentially means that fibres get smaller after each contraction this propels the fetus downwards. the lower segments and cervix dilate with each contraction.
During post partum period the middle muscular layer, which has oblique fibres and maximum number of vessels prevents excessive blood loss as criss cross fibres across the vessels act as living ligatures.
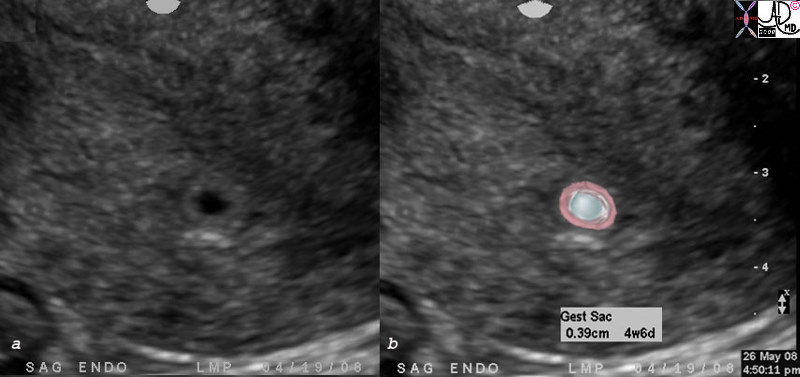
Early IUP |
| 78403c02.8 baby pregnancy OB fetus gestational sac 4 weeks and 6 days early IUP OB endometrium no fetal pole uterus endometrium normal Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD |
