Copyright 2010
Definition
Hydatidiform mole or Molar Pregnancy is a disease of abnormal growth of placental tissue. Most follow a benign course, but a small number of molar pregnancies have the potential for malignancy.
Hydatidiform mole is caused by an aberrant fertilization event.
The result is uncontrolled growth of placental structures called chorionic villi within the uterus.
The structural change is characterized by a mass of vesicles filling and distending the uterus.
The functional change is characterized by the growth of placental tissues from an egg and one or two sperm that have undergone abnormal fertilization without the development of fetal tissues. In a partial mole, a non-viable fetus with multiple anomalies may develop with the placental mass.
The clinical presentation is of abnormal uterine bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy and a uterus that is larger than expected for a fetus’s gestational age. Imaging is useful in the evaluation of suspected hydatidiform mole with ultrasound. Ultrasound characteristically shows a heterogeneous mass with multiple hypoechoic spaces, described as a “snowstorm” pattern.
CXR Frontal View – Trophoblastic Disease – Cystic Metastasis
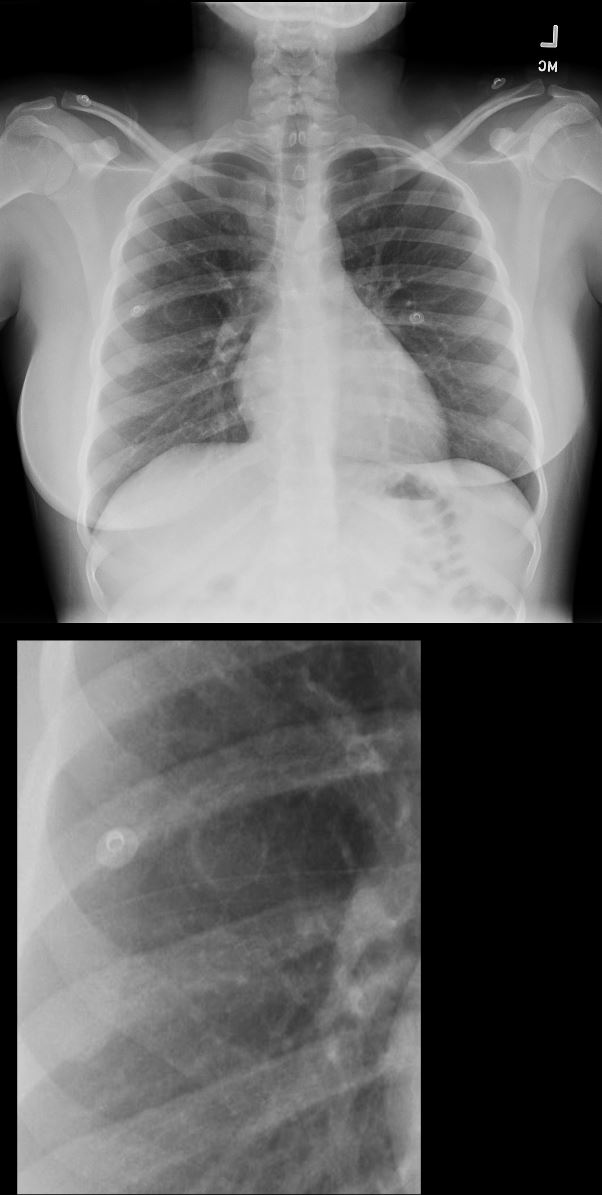
28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days. CXR in the frontal view suggests a cystic structure in the right mid to lower lung field.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136455c
US Vascular Mass in Intrauterine Cavity
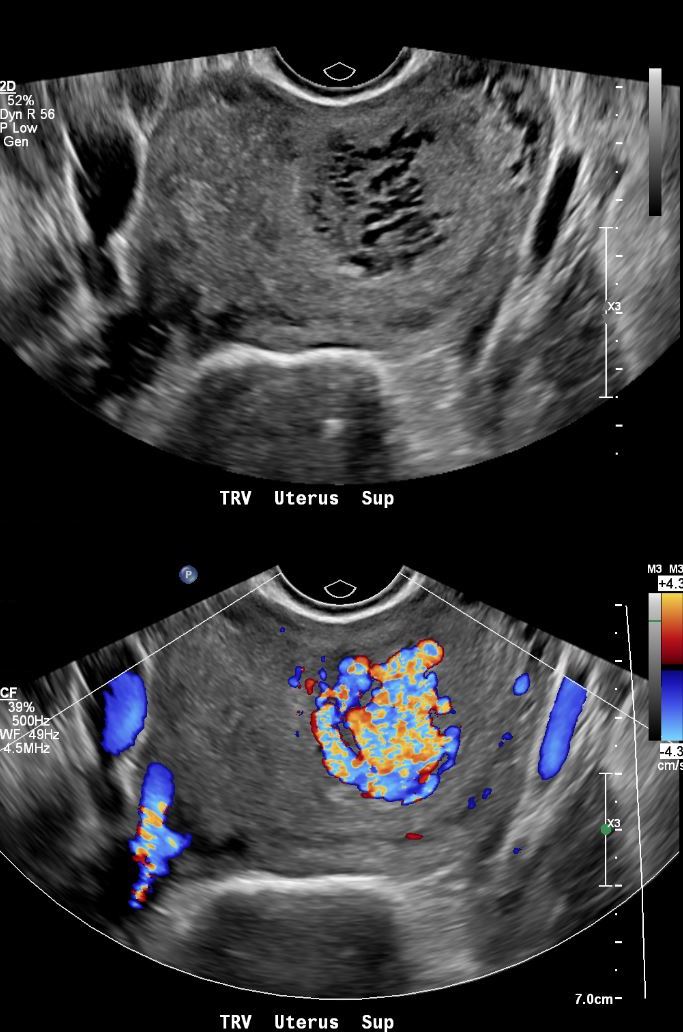
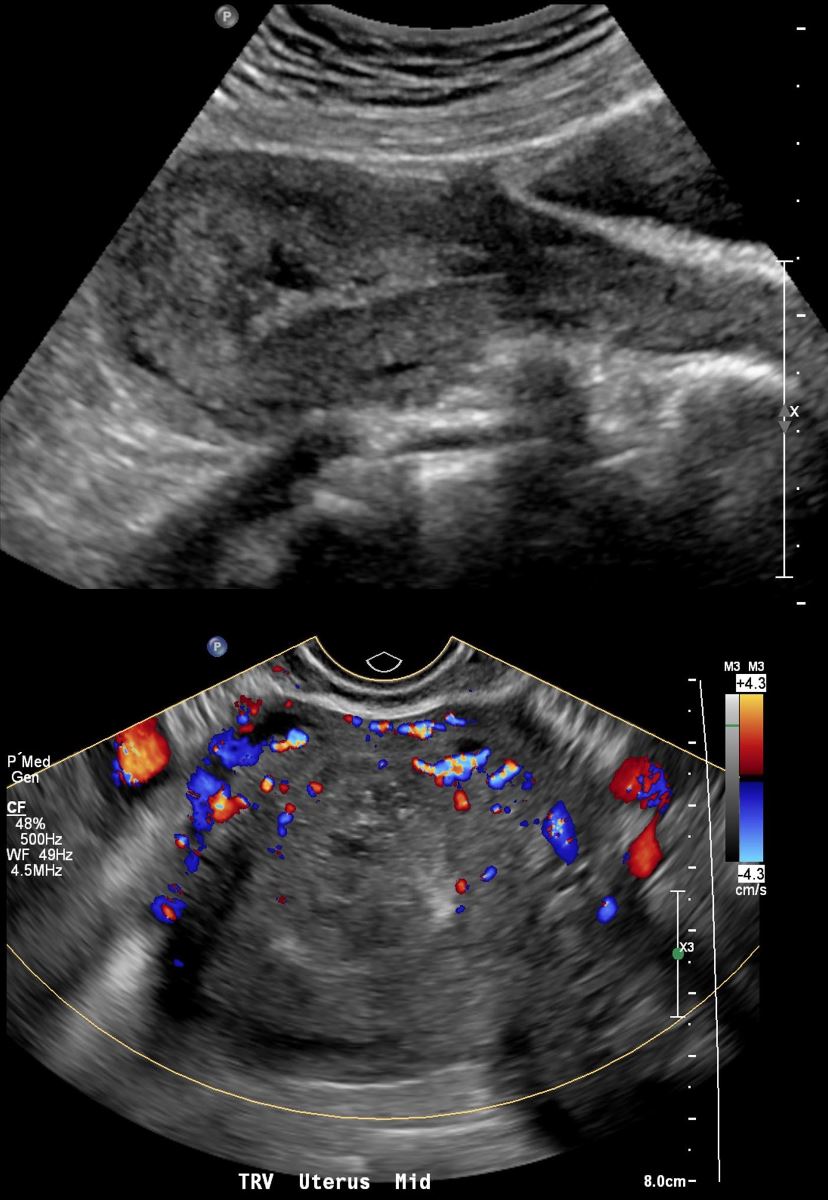
28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Gray scale ultrasound (top image) shows a spongiform mass in the cranial aspect of the uterus Color-flow ultrasound shows a highly vascular mass. Finding are consistent with a hydatiform mole (gestational trophoblastic disease -GTD) but the hCG was only 100.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136457.
US Vascular Mass in Intrauterine Cavity
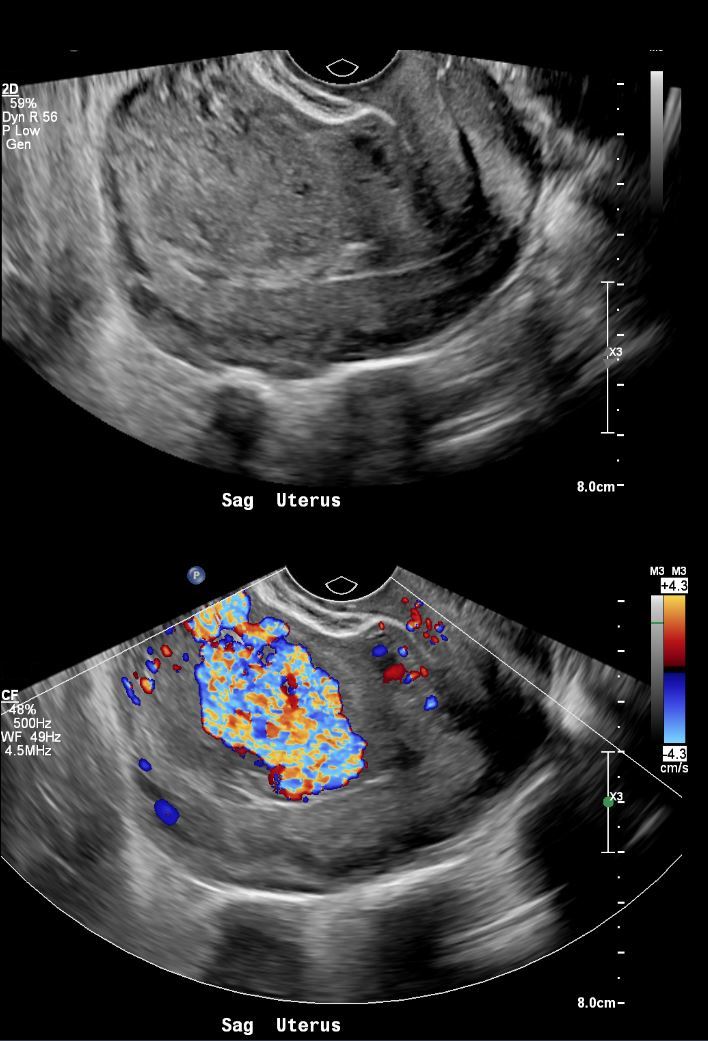
28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Gray scale ultrasound (top image) in the sagittal plane, shows a an isoechoic mass in the cranial aspect of the uterus. Color-flow ultrasound shows a highly vascular mass. Finding are consistent with a hydatiform mole (gestational trophoblastic disease -GTD) but the hCG was only 100.
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136458.
- US current
- no intrauterine pregnancy appreciated
- highly vascular lesion occupying the left uterine fundus and body
- measuring up to 4.0 cm.
- Hcg 98 (down from 100.4 ).
- Admission US
- IMPRESSION:
- No evidence of intrauterine gestation.
- highly vascular lesion occupying the left uterine fundus and body measuring up to 4.0 cm,
- suspicious for uterine arteriovenous malformation.2 days later
- IMPRESSION:
Next day
Angiography Hypervascular Molar pregnancy
Pre and Post Alcohol Ablation

28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days. Angiography of the uterine artery shows a hypervascular mass in the uterine v=cavity without an early draining vein (a,b)
Following alcohol ablation of the feeding distal segmental branch of the left uterine artery, (c,d) reveals that the vascular mass has thrombosed
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136460b01L.
CT Chest – Cavitating Metastatic Trophoblastic Tumor
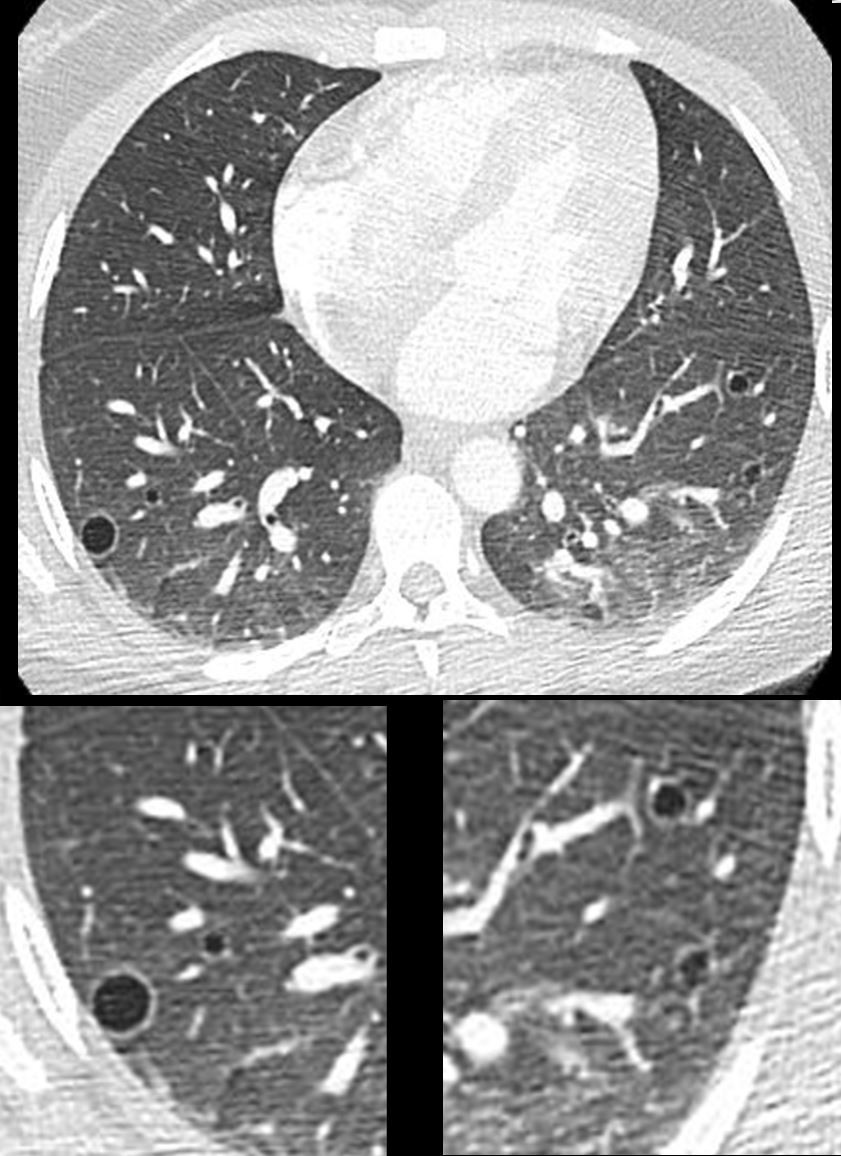
28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days s/p ablation of a vascular molar pregnancy. CT of the chest shows multiple cystic lesions in the lungs bilaterally with slightly thickened walls. Wedge biopsy confirmed a diagnosis of placental site trophoblastic tumor
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136464
Final pathology from uterine biopsies and lung biopsy
-
- consistent with placental site trophoblastic tumor.
MRI Post Ablation
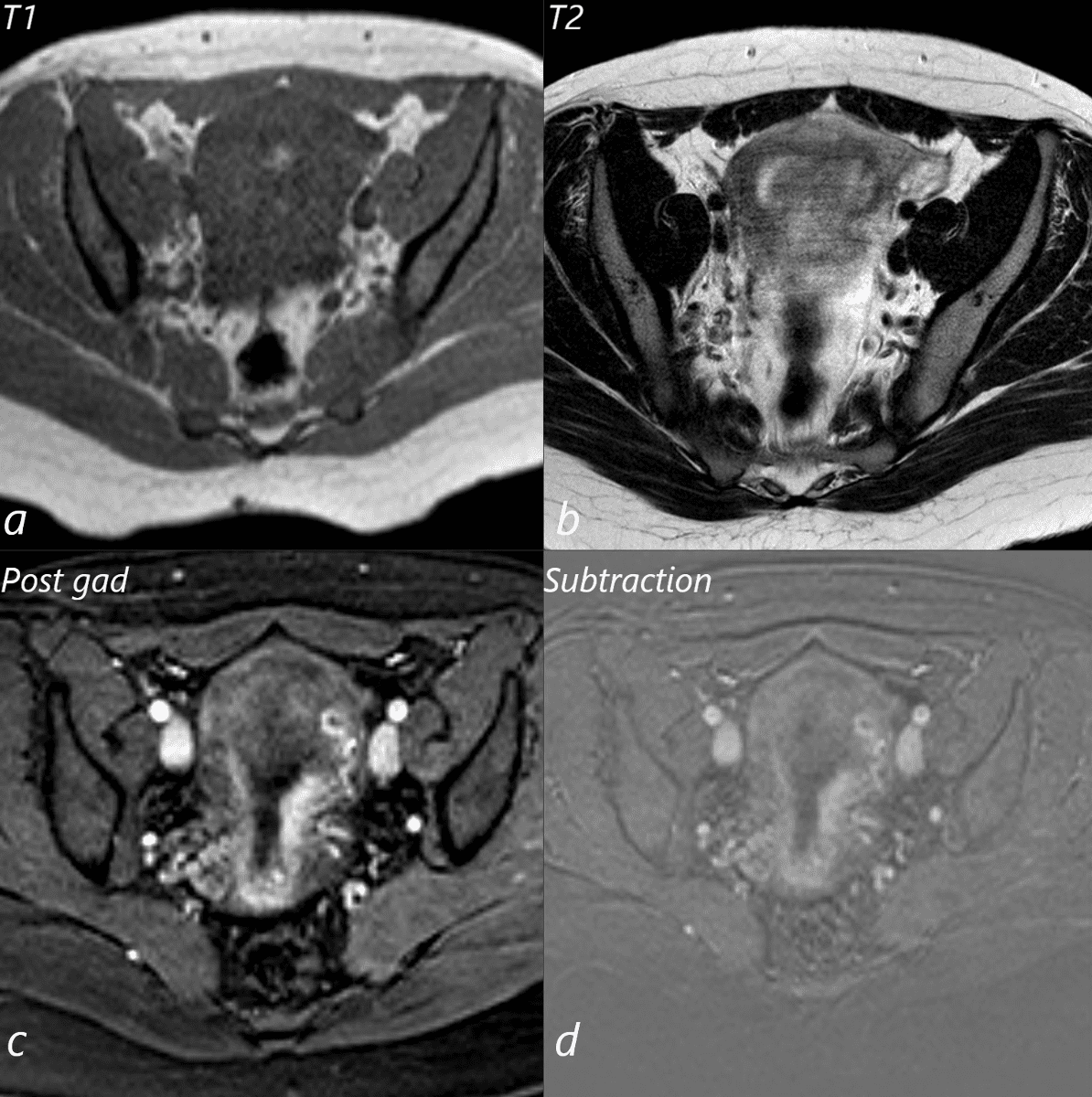
28year old female presents with vaginal bleeding for 3 days s/p ablation of a vascular molar pregnancy. T1 weighted MRI in the axial plane (a) shows a small T1 bright focus in the endometrial cavity, likely representing a small amount of blood. T2 weighted sequence shows heterogeneous signal in the endometrial cavity (b). Following gadolinium administration (c) no vascular mass is appreciated, and absence is confirmed on the subtraction views (d)
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu136460b01L.
US Post Ablation of Placental Trophoblastic Disease
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136467
CT Post Ablation of Placental Trophoblastic Disease
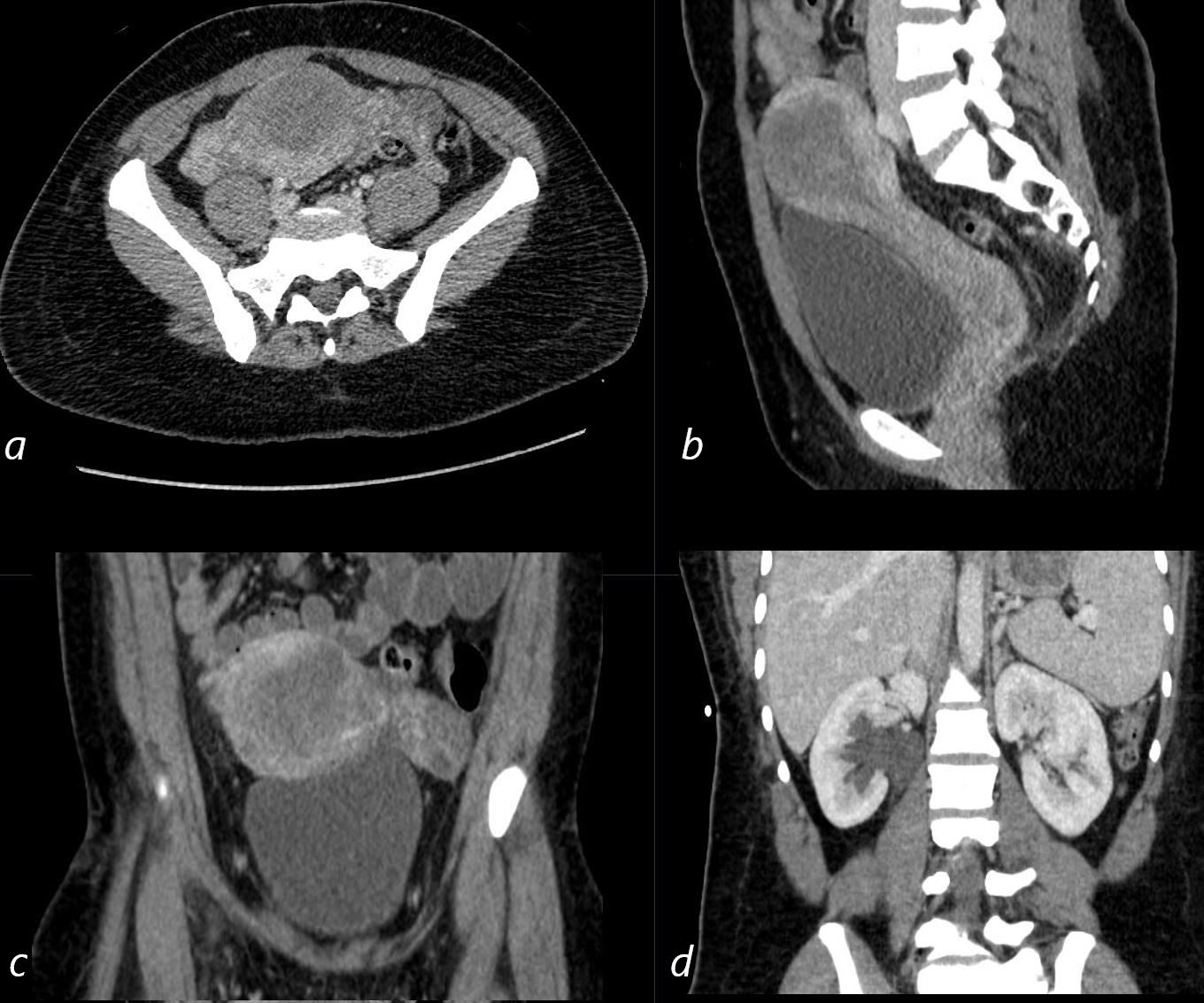
CT Post Ablation of Placental Pelvic ultrasound of a 28year old female with known diagnosis of metastatic placental trophoblastic disease shows heterogeneous changes in the endometrial cavity in axial (a) sagittal (b) and coronal (c) projections. Right sided hydronephrosis is noted
Ashley Davidoff MD TheCommonVein.net 280Lu 136466L
.
Diagnosis is suspected with a combination of clinical presentation and atypical elevation of bhCG, a hormone elevated in pregnancy and a tumor marker for hydatidiform mole.
Treatment for a hydatidiform mole consists of removal of the mass by suction curettage. After removal of a molar pregnancy, levels of bhCG should be monitored for recurrence. In rare cases where an invasive mole develops, a high rate of cure can be achieved with chemotherapy. After removal, subsequent pregnancy and delivery are often possible.
