The Common Vein Copyright 2008t
Introduction
The anterior ligament consists of the vesicouterine fold of peritoneum, which is reflected on to the bladder from the front of the uterus, at the junction of the cervix and body.
The posterior ligament consists of the rectovaginal fold of peritoneum, which is reflected from the back of the posterior fornix of the vagina on to the front of the rectum. It forms the bottom of recto-uterine pouch, laterally it is bound the folds are called called sacrogeniatal or rectouterine folds which have condensed fibrous tissue which attaches to sacrum and constitute a uterosacral ligaments.

Anterior and Posterior Ligaments |
|
This diagram in the sagittal plane illustrates the peritoneal covering (light purple lining) of the uterus reflected. Anteriorly the peritoneal reflection is shallow and a fold or ligament is created called the vesico-uterine fold. A pouch is also formed called the utero-vesical (aka vesico-uterine) pouch Posteriorly the peritoneum is reflected off the rectum in the region of the fornix of the vagina creating a ligament or fold called the recto-uterine fold. A pouch called the recto-uterine pouch (aka cul de sac. pouch of Douglas recto-vaginal pouch Ehrhardt-Cole recess) is formed. This pouch is very important because it is the most posterior and inferior space of the peritoneal cavity and in the supine or upright position it will be the region where fluid will first accumulate. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 14707.2kb04i06.s.4ke06b02Lb.9sh.91s |
The two lateral or broad ligaments (ligamentum latum uteri) pass from the sides of the uterus to the lateral walls of the pelvis. The portion of the broad ligament which stretches from the uterine tube to the level of the ovary is known by the name of the mesosalpinx. Between the fimbriated extremity of the tube and the lower attachment of the broad ligament is a concave rounded margin, called the infundibulopelvic ligament.
The round ligaments (ligamentum teres uteri) are two flattened bands between 10 and 12 cm. in length, situated between the layers of the broad ligament in front of and below the uterine tubes.
The cardinal, Mackenrodt or transverse ligaments is attached to the side of the cervix uteri and to the vault and lateral fornix of the vagina, and is continuous externally with the fibrous tissue which surrounds the pelvic bloodvessels.
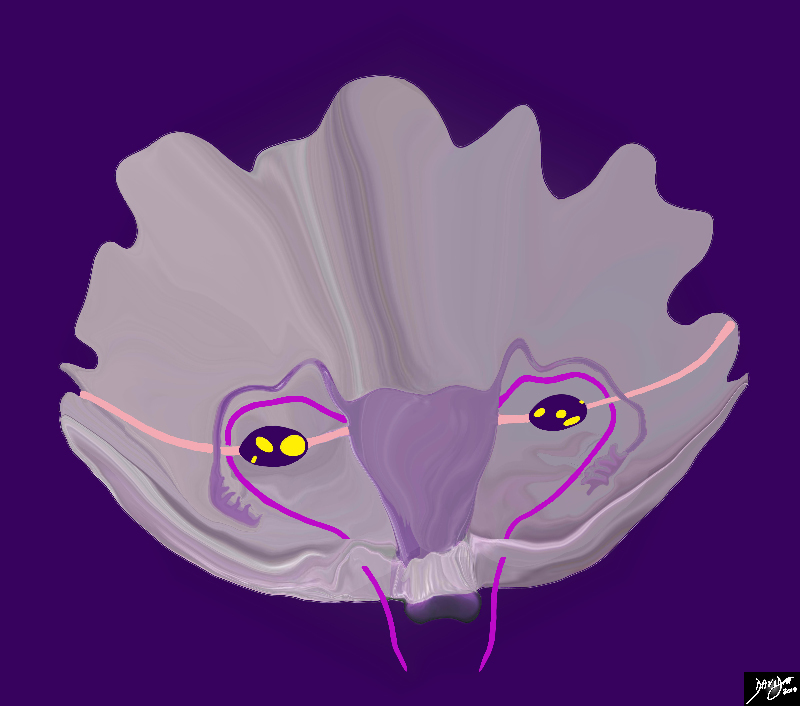
Three Cords Emanating from Near the Cornu |
|
This diagram (behind the scenes and behind the peritoneal covering) illustrates 3 cord like structures that are found near the cornu of the uterus including; the Fallopian tubes (light mauve) the round ligament of the uterus (bright pink) and the ligament of the ovary (light pink) The distal end of the Fallopian tubes end in the fimbriae, while the distal end of the round ligaments enter the inguinal canal. On the other side of the ovary the the ligament of the ovary is called the suspensory ligament of the ovary, aka infundibulopelvic ligament (commonly abbreviated IP ligament or simply IP) and it ends by attaching to the lateral wall of the pelvis. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 04766b05b04.52kd17a09.8s |

Ligaments within the Broad Ligament |
|
This diagram in the sagittal plane demonstrates the broad ligament within which resides the round ligament (shocking pink), the Fallopian tube, and the ovarian ligament. Within the broad ligament the uterine/ovarian artery runs (red), uterine/ovarian vein (blue) lymphatics (yellow) and nerves. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 14707.2kb04i06.s.4ke06b15bL01bh.9s |

Ligaments formed by the Broad Ligament |
|
This diagram in the sagittal plane demonstrates the broad ligament within which resides the round ligament (shocking pink), the Fallopian tube, and the ovarian ligament. There are folds formed by the broad ligament that support the ligaments within it. These include the mesovarium that supports the ovarian ligament, the mesosalpinx that supports the Fallopian tube and the mesometrium that supports the myometrium Within the broad ligament the uterine/ovarian artery runs (red), uterine/ovarian vein (blue) lymphatics (yellow) and nerves. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 14707.2kb04i06.s.4ke06b15bL02bh.9s |
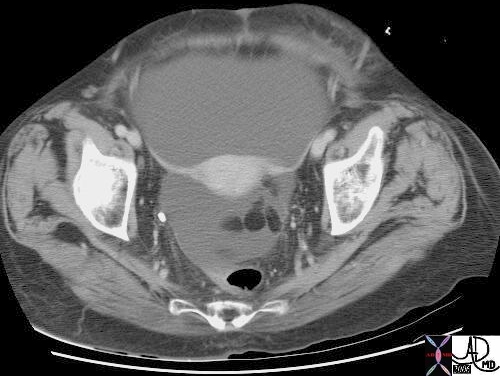
Broad Ligaments Extending from the Uterus to the Pelvic Side Walls |
| 18162 CTscan Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
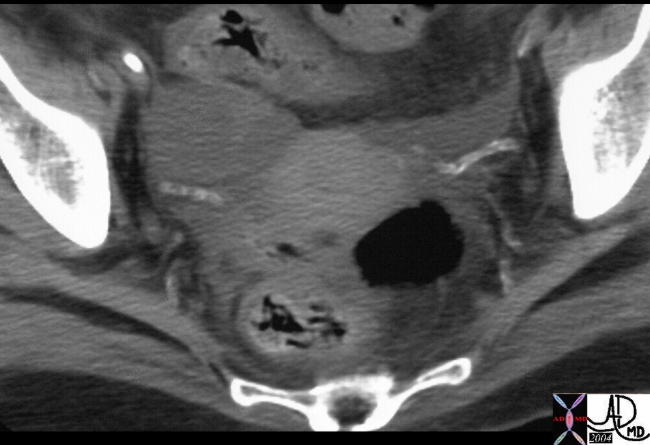
Calcified Round Ligament in a Diabetic Patient |
| 22579 Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD |
Ligaments of Female Pelvis
Broad ligament of uterus – 2 layers of peritoneal covering, from lat margin of uterus –> lat pelvic wall
holds uterus in position
contains: uterine tube, a/v, round ligament, ovarian ligament proper, urete, uterovaginal n. plexus, lymph vessels
Mesovarium – fold of peritoneum that connects ant surface of ovary w/ post layer of broad ligament
Mesosalpinx – fold of broad ligament that suspends the uterine tube
Mesometrium- fold of broad lig below mesosalpinx, and meso-ovarium, lat wall of uterus –> pelvic wall
Proper Ovarian ligament – fibromusc cord from uterine end of ovary –> side of uterus below uterine tube w/in broad lig
Suspensory ligament of ovary – band of peritoneum that runs sup/lat from end of ovary –> pelvic wall, has ovarian a/v, lymph vessels
Lat/Transverse Cervical (Cardinal) Lig of Uterus (aka ligament of Mackenrodt’s) – fibromuscular condensations of pelvic fascia from cervix (hence, cervical) & lat fornix of vagina –> pelvic wall, run w/in parametrium of uterus
Parametrium – fibrous CT that runs w/in mesometrium, connects uterus to lat pelvic wall
Paracolpium – fibrous CT that connects the lat wall of vagina –> lat pelvic wall, fibers merge w/ those of para cysticum (for bladder)
Pubocervical ligament – firm bands of CT from post surface of pubis –> cervix of uterus
Sacrocervical(uterine) ligament – firm fibromuscular bands of pelvic fascia from lower end of sacrum –> to cervix, upper end of vagina *palpable in rectal exam
Pubovesical ligament – pelvic fascia bands from neck of bladder (or prostate in male) –> pelvic bone
Rectouterine ligament – holds cervis back and up and sometimes elevate a shelf-like fold of pertioneum (recto-uterine folds – called sacro-genital folds in male)
isthmus of uterus –> post wall of pelvis, lat to rectum
