Definition
Bicornuate uterus is a congenital anomaly of the uterus caused by incomplete fusion of the mullerian ducts during embryonic development.
The result is a uterus with 2 separate horns that fuse above a single cervix.
The structural change is characterized by an abnormally small uterine cavity that separates into the two uterine horns.
The functional change is characterized by limitation of space for fetal growth during pregnancy.
As a result women present clinically with repeated loss of pregnancy in the second trimester, or preterm labor and delivery. However, many women with bicornuate uterus can carry a pregnancy to term.
Imaging modalities used to evaluate uterine abnormalities include sonohysterography, hysterosalpingography, and MRI. MRI is useful as it allows for differentiation of septate and bicornuate uterus, as wells as concurrent evaluation of the urinary tract.
Diagnosis is made with these imaging studies, combined with laparoscopy if necessary. For women who cannot carry a pregnancy, a uterine unification procedure (metroplasty) can be performed. Delivery by caesarian section is necessary after these procedures to eliminate the risk of uterine rupture.
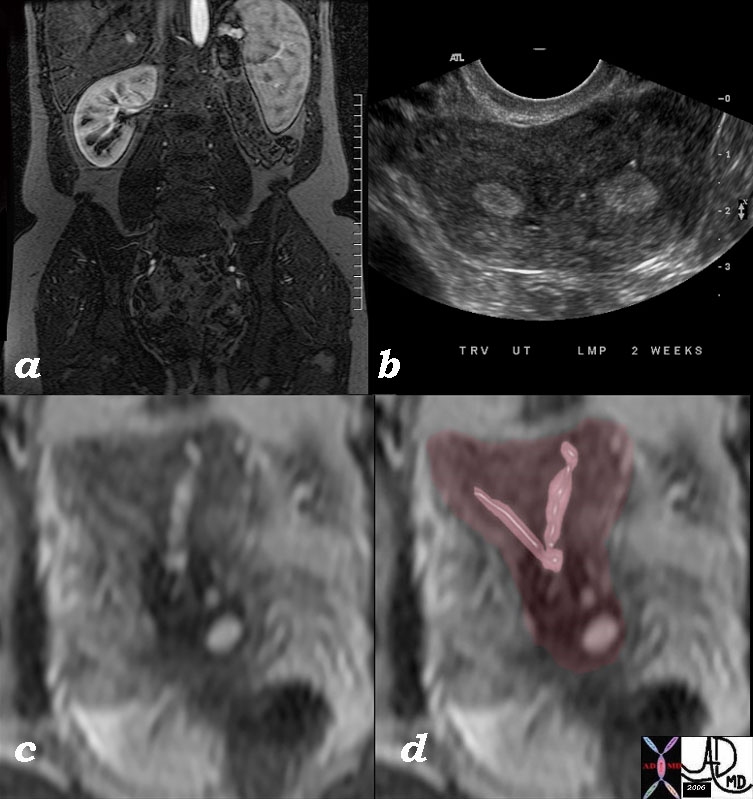
Bicornuate Uterus T2 Weighted Image |
|
The series of images from a young adult female with Bicornuate uterus with agenesis of the left kidney. Image a is a coronal T1 weighted contrast enhanced image that shows absence of the left kidney. Image b is an ultrasound in transverse dimension that shows two endometrial cavities. Image c is a T2 weighted image that shows 2 separate horns that fuse above a single cervix and overlaid in pink in image d These findings are consistent with bicornuate uterus with agenesis of the left kidney. Combined congenital anomalies of the uterus and renal system are a well known association. 46527c01 Image Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD Copyright |
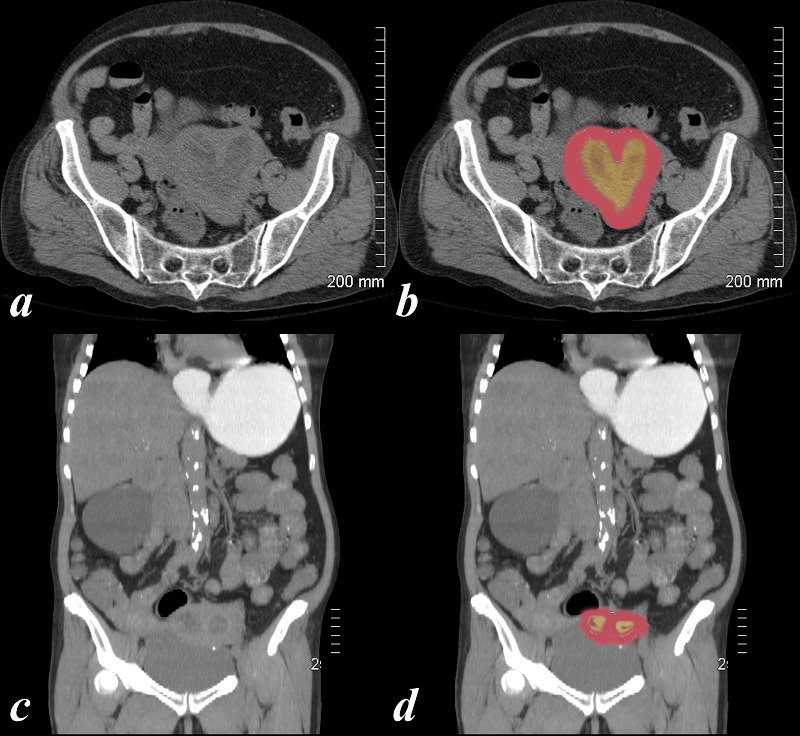
Bicornuate with Cervical Carcinoma |
|
74 year old female with bicornuate uterus and dilated endometrial cavities Diagnosis is carcinoma of the cervix with obstruction . Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2009 all rights reserved 83438c01.8s |
Bicornuate uterus occurs when there is failure of fusion of bilateral mullerian system system. This could give rise to multiple abnormalities depending on proximal or distal involvement.
